Sleep apnea is a serious condition that can significantly impact your life if left untreated. While it can be considered a disability in some cases, the key to managing it lies in recognizing the symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment and making lifestyle changes.
What is Sleep Apnea?
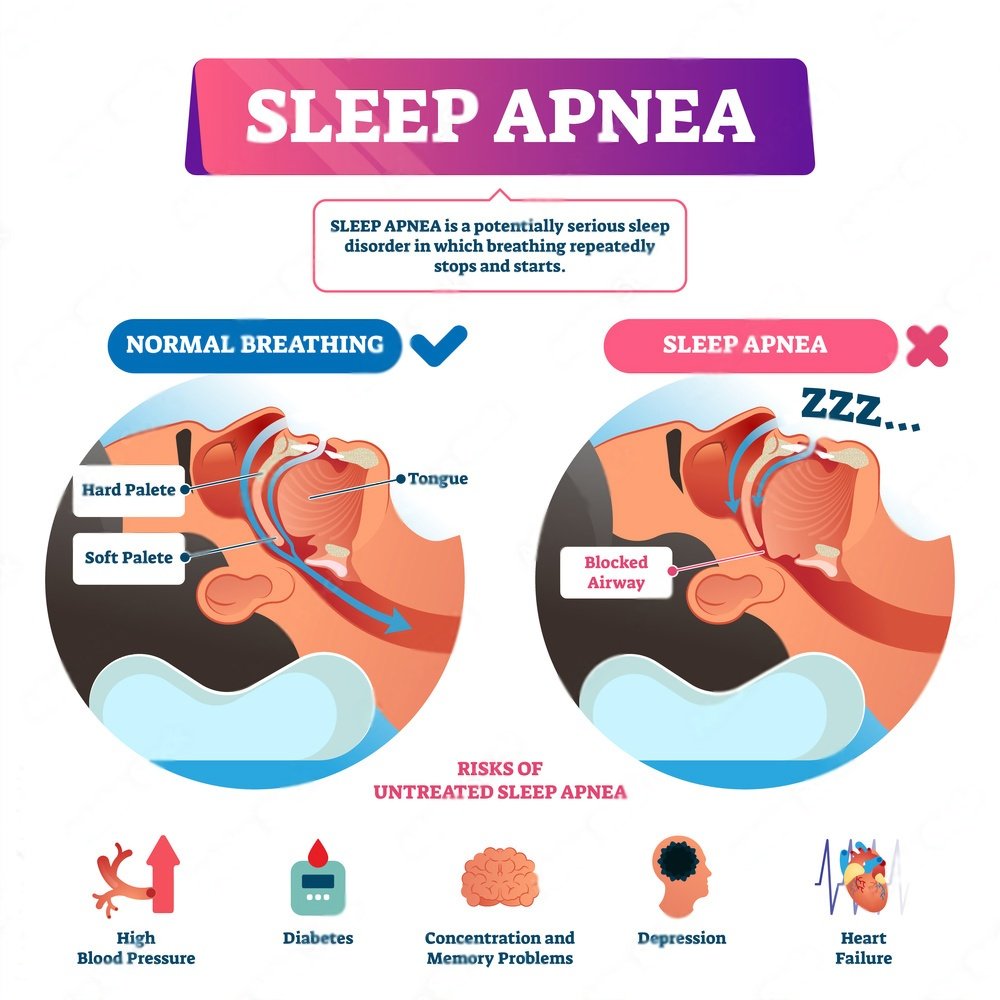
Sleep apnea is a condition that affects your breathing while you sleep. It happens when the muscles in your throat relax too much during sleep, causing your airway to become blocked. This blockage leads to pauses in breathing or shallow breaths, which can happen multiple times throughout the night.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
There are two main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type. It occurs when the throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This type occurs when the brain doesn’t send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea:
People with sleep apnea often snore loudly and feel tired even after a full night’s sleep.
Common symptoms include:
- Loud snoring
- Episodes of stopped breathing during sleep
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Waking up with a dry mouth
- Morning headache
- Difficulty staying asleep (insomnia)
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- Difficulty paying attention while awake
- Irritability
Is Sleep Apnea a Disability?
The Social Security Administration (SSA) does not automatically consider sleep apnea a disability. If the condition severely impacts your ability to work and perform daily activities, you might qualify for disability benefits under certain circumstances.
Here’s what you need to know:
Criteria for Disability:
To qualify for disability benefits, the SSA requires that your sleep apnea significantly limits your ability to perform basic work activities. This could include difficulties with concentration, memory, or physical stamina.
Additionally, the SSA considers how well your condition is controlled with treatment and whether you have other related medical issues, such as heart disease or high blood pressure.
Impact on Daily Life:
Sleep apnea can severely impact your quality of life. It can lead to chronic fatigue, making it difficult to concentrate, stay awake during the day, or perform tasks efficiently. If untreated, it can contribute to serious health issues such as heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. These complications can make managing daily activities challenging.
Medical Evidence:
To be considered for disability benefits, you need to provide comprehensive medical evidence. This includes documentation of your diagnosis, treatment history, and how the condition affects your daily life and ability to work.
The SSA looks at medical records, doctor’s notes, sleep study results, and any other relevant information to assess your case.
Managing Sleep Apnea:
Medical Treatments:
There are several treatments available to manage sleep apnea:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): This is the most common treatment. A CPAP machine delivers a steady stream of air through a mask to keep the airway open.
Lifestyle Changes: Losing weight, avoiding alcohol, and quitting smoking can help reduce symptoms.
Dental Devices: These can help keep the airway open by bringing the jaw forward during sleep.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove tissue or adjust the structure of the airway.
Self-Care Strategies:
In addition to medical treatments, there are self-care strategies that can help manage sleep apnea:
Sleeping on Your Side: This can prevent the airway from becoming blocked.
Using a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can reduce congestion and improve breathing.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Being overweight can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing sleep apnea can lead to a better quality of life and improved overall health. If you think you might have sleep apnea, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
